We will be discussing the core functions and architecture of SCADA Systems. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) is a key infrastructure for our Nectec’s pick and place machine NT series. Its core functions include five key steps. First step is data acquisition. It involves real-time collection of production line data through distributed sensor networks (such as temperature, vibration, current, visual inspection, etc.), with a sampling frequency typically ≥10Hz, ensuring high-precision monitoring. Supports multiple industrial communication protocols (Modbus, OPC UA, Profinet, CAN bus, etc.), compatible with equipment from different manufacturers. Second step is data processing and analyzing. It involves data cleansing (removing outliers, filtering noise), real-time calculation (OEE, MTBF, defect rate, and other KPIs) and rule-based automated alerts (such as SPC limit warnings). Third step is visualized monitoring. It involves dynamic HMI (Human Machine Interface) displays production line status and visualization tools such as trend charts, dashboards, and alarm logs. Fourth step is production scheduling, quality traceability, and energy efficiency optimization based on data analysis, along with optimization of production scheduling through integration with MES/ERP systems. Fifth step is the transparency in the production process. It involves real-time order progress tracking, automatic verification of process parameters and immediate interception of quality defects. Next, the advantages of SCADA systems are breaking down into five aspects. First aspect is the core applications of SCADA in surface mount interconnection. It involves real-time data acquisition, remote monitoring and intelligent control, as well as optimization of production efficiency and quality control. Second aspect is real-time data collection and monitoring. The SCADA system uses sensors and PLCs to collect key parameters in real time during the production process of the pick-and-place machine, such as temperature, pressure, and equipment status, and transmits the data to the central control room for visualization.
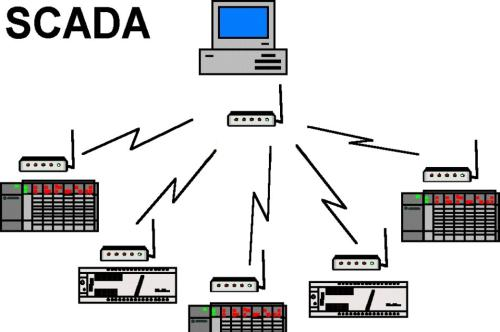
For example, our Nectec’s pick-and-place machines NT series in the electronics industry can reach 100%, enabling real-time tracking of production progress and automatic verification of process parameters. Third aspect is remote control and anomaly alerts. It involves the system to support remote adjustment of device parameters and sets more than 500 abnormal judgment rules to achieve real-time early warning. Fourth aspect is production efficiency and quality control. Where optimize production processes through data analysis and reduce rework rates by immediately intercepting quality defects. In addition, the system can generate energy consumption heat maps to help identify high-energy consumption links and optimize energy use. Last aspect of the advantages is equipment lifecycle management. SCADA supports real-time monitoring of equipment utilization, failure rates, and other indicators helps enterprises achieve intelligent equipment maintenance.





